Smart home technology trends are rapidly transforming how we live and interact with our homes. From the early days of basic automation to today’s sophisticated AI-powered systems, the evolution has been remarkable. This exploration delves into the key advancements, emerging connectivity trends, and the future implications of this technology.
The integration of AI and automation is playing a crucial role in personalizing and optimizing smart home experiences. Moreover, security and privacy concerns are paramount, necessitating robust protocols and solutions. Smart homes are also increasingly integrating with other smart devices and systems, impacting energy management and potentially revolutionizing our living environments.
Evolution of Smart Home Technology
The concept of a smart home, where devices and systems interact seamlessly to enhance convenience and efficiency, has evolved significantly over time. Early ideas were largely theoretical, but technological advancements have progressively brought these concepts to life, leading to today’s sophisticated and interconnected smart home systems. This evolution reflects not only technological progress but also changing consumer needs and expectations.The initial seeds of smart home technology were planted decades ago, with various innovations laying the groundwork for the sophisticated systems we see today.
From rudimentary automation to sophisticated AI-powered solutions, the journey has been marked by incremental progress and transformative breakthroughs. Understanding this evolution provides valuable insight into the future direction of smart home technology and its potential to reshape how we live and interact with our environments.
Early Concepts and Pioneers
Early smart home concepts focused on automating basic tasks, often utilizing electromechanical relays and timers. These early systems were primarily limited to controlling lighting and appliances via simple on/off switches or schedules. The technology was often expensive and complex, making widespread adoption challenging. However, these early attempts demonstrated the fundamental desire to automate and improve household functionality.
For example, pre-programmed timers for lights or appliances were rudimentary forms of automation, laying the groundwork for more advanced control systems.
Key Milestones and Innovations
The development of microcontrollers, sensors, and wireless communication technologies significantly propelled smart home evolution. The emergence of the internet and the proliferation of personal computers paved the way for more sophisticated control systems. The development of the internet of things (IoT) created a platform for interconnected devices, leading to the integration of various home systems. These developments have transformed the way we interact with our homes, making it possible to control lighting, temperature, security, and entertainment from a central point, often via smartphones.
Comparison of Early and Current Implementations
Early smart home concepts were largely limited to individual devices performing isolated tasks. Today’s implementations encompass sophisticated ecosystems, where devices communicate and interact seamlessly. This interconnectedness allows for complex automation, personalized experiences, and enhanced energy efficiency. For example, early thermostat control systems were limited to pre-set schedules, whereas modern systems use algorithms to optimize energy consumption based on real-time data.
Evolution of Devices and Systems
Early smart home devices were often standalone and operated independently. As technology advanced, these devices integrated with each other, creating a unified system. For example, a smart thermostat initially controlled only temperature, but now integrates with other smart devices to optimize energy use based on factors like lighting, occupancy, and weather conditions. This integration has transformed how we interact with and manage our homes.
Table: Evolution of Smart Home Technology
| Year | Device | Functionality | Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1980s | Programmable thermostats | Basic temperature control, scheduled adjustments | Early demonstration of automation potential. |
| 1990s | Home automation systems | Integration of lighting, security, and appliances | Expanded functionalities, but limited by technology. |
| 2000s | Smart thermostats, lighting systems | Remote control, energy optimization | Increased accessibility and efficiency. |
| 2010s | Smart speakers, hubs, IoT devices | Voice control, seamless integration, enhanced security | Expanded control, more intuitive user experience. |
| 2020s | AI-powered assistants, predictive maintenance | Personalized experiences, enhanced safety, anticipatory actions | Enhanced user convenience, increased automation sophistication. |
Emerging Trends in Connectivity
Smart home technology is rapidly evolving, and connectivity is a key driver of this evolution. The quest for seamless integration and enhanced responsiveness in smart homes is pushing innovation in various areas, from high-speed networks to decentralized architectures. This section explores the current and future trends in smart home connectivity, highlighting the impact of cutting-edge technologies and the role of standardized protocols.
Current and Future Trends in Smart Home Connectivity
The future of smart home connectivity is characterized by a move towards faster, more reliable, and more versatile systems. Existing Wi-Fi standards are being augmented by newer technologies, and the integration of decentralized networks is gaining traction. The aim is to create a more responsive, reliable, and interoperable smart home ecosystem.
Impact of 5G and Wi-Fi 6 Technologies
G and Wi-Fi 6 are significantly impacting smart home devices. 5G’s high bandwidth and low latency enable real-time communication for demanding applications like video conferencing and high-definition video streaming within the home. Wi-Fi 6 enhances network capacity and efficiency, supporting a larger number of connected devices simultaneously. These advancements are crucial for supporting the increasing complexity of modern smart homes.
Examples include the ability to stream high-quality video from security cameras in real-time, or to have multiple devices connected to the network without experiencing slowdowns.
Role of IoT Protocols in Enabling Seamless Interoperability
IoT protocols play a vital role in ensuring seamless interoperability between different smart home devices. Standards like Zigbee, Z-Wave, and Matter facilitate communication and data exchange between devices from various manufacturers. This interoperability is key to a more integrated and user-friendly smart home experience. The Matter protocol, for instance, is designed to allow devices from different brands to work together seamlessly.
Potential for Decentralized Networks in Future Smart Homes
Decentralized networks have the potential to revolutionize smart home connectivity. These networks distribute the processing and management of data, reducing reliance on central hubs and improving resilience to outages. A decentralized system could provide a more robust and secure smart home network, even in the face of disruptions. For example, in a future smart home, local sensors could analyze and respond to environmental changes without constant communication with a central hub.
Smart home tech is evolving rapidly, offering increasingly sophisticated features. One key area is how these advancements impact affordable interior decoration, like choosing energy-efficient lighting or automated blinds. This translates to greater design flexibility and control within a budget-conscious framework. The future of smart homes is definitely interesting to consider, given these ongoing trends.
This could enhance responsiveness and efficiency.
Comparison of Connectivity Options for Smart Homes
| Connectivity Option | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Wi-Fi | Widely available, established infrastructure, relatively low cost. | Can be susceptible to interference, speed limitations with numerous devices, may not be suitable for high-bandwidth applications. |
| 5G | High bandwidth, low latency, supports high-definition video, real-time applications. | Requires specialized infrastructure, higher initial cost for implementation, limited range in some cases. |
| Zigbee | Low power consumption, suitable for battery-powered devices, good range for home use. | Lower bandwidth compared to other options, potentially slower speeds for data-intensive applications. |
| Z-Wave | Robust security features, reliable communication, good range for home use. | Lower bandwidth than Wi-Fi, can be more complex to set up for some users. |
| Matter | Promotes interoperability between devices from different manufacturers, simplifies setup and control. | Still a relatively new standard, adoption rate is growing, limited device support initially. |
AI Integration and Automation
Artificial intelligence (AI) is rapidly transforming smart homes, moving beyond simple automation to sophisticated, personalized experiences. AI’s ability to learn and adapt allows smart home systems to anticipate needs and optimize efficiency, creating a more responsive and user-friendly environment. This integration fosters a seamless interaction between technology and daily life.
Role of AI in Enhancing Smart Home Automation
AI algorithms are crucial for optimizing smart home automation. They enable devices to react dynamically to various environmental factors, such as lighting conditions, temperature fluctuations, and occupancy levels. This proactive response enhances the automation’s effectiveness and user experience, ensuring that the home adjusts automatically to the resident’s needs and preferences.
Machine Learning Algorithms Personalizing Smart Home Experiences
Machine learning (ML) algorithms play a pivotal role in personalizing smart home experiences. These algorithms analyze user behavior patterns, preferences, and routines to anticipate needs and automatically adjust settings accordingly. For example, a system might learn that the user typically lowers the thermostat by 2 degrees before bed, and adjust accordingly, optimizing energy consumption and comfort. ML also allows for proactive adjustments based on weather patterns or other external factors, further improving the user experience.
AI-Powered Predictive Maintenance in Smart Home Devices
AI can predict potential malfunctions in smart home devices before they occur. By analyzing data from sensors and historical usage patterns, AI algorithms can identify patterns indicative of device wear and tear. This proactive maintenance capability reduces the likelihood of unexpected breakdowns and extends the lifespan of smart home components. This predictive maintenance is vital for long-term cost savings and a seamless home experience.
Impact of Voice Assistants on Smart Home Control and Automation
Voice assistants are significantly impacting smart home control and automation. These assistants provide a hands-free and intuitive way to interact with smart home devices. They can be used to control lighting, adjust temperature, play music, and manage other functions simply by voice commands. This hands-free interaction enhances user convenience and responsiveness.
Example of an AI-Powered Smart Home Automation Scenario
Imagine a smart home where the AI system learns the resident’s daily schedule. The system anticipates the need for preheating the home before a morning commute, automatically adjusting the thermostat based on the resident’s departure time. Upon the resident’s arrival, the lights dim gradually to a pre-set level, and the music system starts playing a preferred playlist. This proactive and personalized experience creates a welcoming and efficient home environment.
The system can even learn to anticipate needs based on weather patterns, such as adjusting the heating and cooling to match external temperatures.
Security and Privacy Concerns

Smart home technology, while offering convenience and efficiency, presents significant security and privacy challenges. The interconnected nature of these systems, often relying on vulnerable internet connections, creates avenues for malicious actors to compromise devices and access sensitive information. Understanding these risks and implementing robust security measures is crucial for safeguarding personal data and maintaining trust in smart home ecosystems.
Security Vulnerabilities in Smart Home Ecosystems
Smart home devices, often lacking robust security features, are vulnerable to various attacks. Compromised devices can be used to gain access to the entire network, potentially exposing sensitive data like financial information, health records, and personal communications. Furthermore, vulnerabilities in the network’s infrastructure, such as weak passwords or outdated firmware, can be exploited by attackers. The interconnected nature of these systems amplifies the risk, as a breach in one device can lead to a domino effect, impacting the entire home network.
Importance of Data Encryption and Access Controls
Data encryption plays a critical role in safeguarding sensitive information transmitted between devices and the cloud. Strong encryption protocols, such as end-to-end encryption, ensure that only authorized parties can access data, even if the communication channel is compromised. Furthermore, robust access controls are essential to limit access to sensitive data and prevent unauthorized users from gaining control of smart home devices.
This includes multi-factor authentication and strong, unique passwords for each device.
Potential Privacy Risks Associated with Smart Home Devices
Smart home devices constantly collect data about users’ habits, preferences, and surroundings. This data, if not handled responsibly, can be used to create detailed profiles of individuals, potentially compromising their privacy. For instance, a smart thermostat gathering information about user routines could be exploited to target individuals with personalized advertising or even malicious schemes. Furthermore, the potential for data breaches and unauthorized access to this data underscores the need for careful consideration of privacy policies and data handling practices by manufacturers.
Importance of Robust Security Protocols for Smart Home Devices
Implementing robust security protocols is crucial for mitigating security risks. These protocols should include regular firmware updates to address known vulnerabilities, strong encryption for data transmission, and multi-factor authentication for user accounts. Furthermore, manufacturers should prioritize security during the design and development process to prevent vulnerabilities from being exploited. Regular security audits and penetration testing can help identify potential weaknesses and ensure that the system remains secure over time.
Methods to Enhance the Security of a Smart Home Network
Strengthening the security of a smart home network requires a multi-faceted approach. This includes using strong and unique passwords for all devices and accounts, enabling two-factor authentication whenever possible, and regularly updating firmware on all connected devices. Implementing a strong router firewall and utilizing a virtual private network (VPN) can further enhance security by encrypting internet traffic and creating a secure connection.
Regularly reviewing and updating security settings on smart home devices is also critical. A dedicated smart home security system with advanced features can further protect the network from threats.
Integration with Other Smart Devices: Smart Home Technology Trends
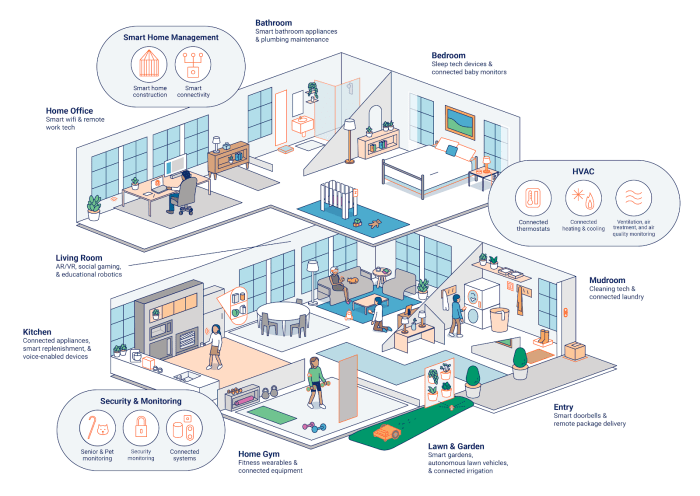
Smart home technology is rapidly evolving, moving beyond individual devices to encompass a broader ecosystem of interconnected smart appliances. This seamless integration fosters a more intelligent and responsive home environment, optimizing energy use, enhancing security, and improving overall comfort. This trend is driven by advancements in communication protocols and the growing demand for interconnected systems.
Seamless Integration Between Smart Home and Other Smart Appliances
The interconnected nature of smart homes extends beyond the confines of the house itself. Integration with other smart appliances, such as smart refrigerators, ovens, and washing machines, allows for a more holistic and automated approach to household management. For example, a smart refrigerator can automatically order groceries based on inventory levels, and a smart oven can preheat based on a schedule received from the smart home system.
This level of interoperability is improving efficiency and reducing the need for manual intervention.
Integration with Smart Grids and Renewable Energy Sources
Smart homes are increasingly integrating with smart grids, enabling real-time energy management and optimization. This integration allows for seamless communication between the home’s energy consumption and the broader grid, facilitating the integration of renewable energy sources like solar panels. The home can adjust energy usage in response to grid demands, potentially earning credits or participating in demand response programs.
This bi-directional communication is key to a more sustainable and responsive energy ecosystem.
Comparison of Smart Home and Smart Office Systems Integration
While smart home systems are becoming more sophisticated, they often lack the comprehensive integration found in some smart office systems. Smart office systems often integrate more deeply with enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems and other business applications, leading to greater automation and efficiency in tasks like scheduling and resource allocation. Smart homes, in contrast, primarily focus on individual comfort and convenience, although the integration with smart grids is an example of a growing interconnection with external systems.
Examples of Enhancing Home Energy Management
Smart home technology is revolutionizing home energy management. Smart thermostats can learn user preferences and adjust temperatures automatically, reducing energy waste. Smart lighting systems can dim or turn off lights based on occupancy and natural light levels, leading to significant energy savings. Smart appliances can be scheduled to run during off-peak hours, further optimizing energy consumption. For example, a smart washing machine can be scheduled to run during the night, when electricity rates are lower.
Table of Smart Home Device Integrations
| Device Type | Potential Integrations |
|---|---|
| Smart Thermostat | Smart lighting, smart appliances, smart energy grid |
| Smart Lighting | Smart thermostats, smart home security system, smart assistants |
| Smart Appliances (Refrigerator, Oven, Washer) | Smart home system, smart grocery delivery services, smart energy grid |
| Smart Security System | Smart lighting, smart locks, smart home system, smart assistants |
| Smart Speakers/Assistants | All other smart home devices, smart home system, calendar, scheduling, and reminders |
Smart Home Devices and the Future of Living
Smart homes are rapidly evolving, moving beyond simple automation to encompass a more holistic approach to living. They are increasingly designed to cater to diverse lifestyles, needs, and preferences, aiming to enhance comfort, convenience, and safety within various living environments. This evolution touches upon aspects like accessibility for individuals with disabilities, sustainability, and tailored experiences for specific demographics.
Future of Smart Homes in Different Living Environments
Smart home technology is adapting to the varied needs of different living environments. For example, smart homes in apartments often prioritize space-saving solutions and energy efficiency. Homes in rural areas may focus on features like remote security monitoring and automated irrigation systems. Customizable smart home solutions cater to the unique requirements of these diverse living environments.
Smart Homes and Accessibility for Individuals with Disabilities
Smart home technology has a significant role to play in improving accessibility for individuals with disabilities. Features such as voice-activated controls, automated lighting, and adaptable temperature settings can greatly enhance independence and safety. Smart home devices can also be configured to assist with tasks like navigation and communication. This increased independence empowers individuals with disabilities to live more fulfilling lives within their own homes.
Smart Homes and Sustainable Living Practices
Smart homes are becoming increasingly integrated with sustainable living practices. Automated systems can optimize energy consumption, detect and address leaks, and monitor water usage, contributing to a reduced environmental footprint. Smart appliances, like smart refrigerators that automatically adjust temperature based on usage, contribute to overall energy efficiency. By integrating sustainable features, smart homes help promote eco-friendly living.
Smart Home Designed for a Family with Young Children
A smart home designed for a family with young children prioritizes safety, convenience, and child-friendly features. Smart locks with parental controls ensure security, while automated lighting and temperature settings can enhance comfort. Integrated entertainment systems with age-appropriate content filtering cater to children’s needs. Motion sensors and safety cameras in key areas contribute to peace of mind. A dedicated learning space equipped with smart interactive tools promotes education and learning.
The Impact of Smart Home Technology on the Economy

Smart home technology is rapidly transforming the residential and commercial landscapes, driving significant economic ripples. This evolution presents exciting opportunities for job creation, market growth, and improved consumer experiences. From energy efficiency gains to increased convenience, smart home solutions are poised to reshape the global economy.
Economic Implications of Smart Home Adoption
The adoption of smart home technology has several intertwined economic implications. Firstly, it stimulates innovation and development within the tech sector, fostering new industries and specialized skillsets. Secondly, the expansion of the smart home market leads to increased demand for related services, from installation and maintenance to software updates and support. Finally, the integration of smart home technology into existing infrastructure can potentially lead to significant cost savings and efficiency gains for both consumers and businesses.
Impact on Job Creation and Market Growth
The smart home sector is creating new jobs in diverse areas, from software development and hardware engineering to installation and maintenance. This growth is anticipated to continue as smart home devices become more sophisticated and integrated into daily life. The expansion of the market also drives demand for skilled professionals in related fields, such as cybersecurity and data analytics.
New roles are emerging that cater specifically to the demands of smart home technologies.
Economic Benefits for Consumers
Smart home technologies offer consumers a multitude of economic advantages. Improved energy efficiency translates to lower utility bills, enhancing their financial well-being. Smart home automation systems can reduce labor costs associated with routine household tasks. The increased convenience and security provided by smart home solutions also contribute to overall cost savings. Smart appliances and devices can automate complex processes, reducing the time spent on routine chores.
Economic Benefits for Businesses
Smart home technology offers businesses opportunities to expand their offerings and services. Home builders can integrate smart home features into new constructions, adding value and increasing home appeal. Retailers can expand their product lines to include smart home accessories, while service providers can offer installation and maintenance packages. Smart home technology also allows businesses to gain insights into consumer behavior, allowing for more targeted marketing and improved service delivery.
Market Value and Growth Potential of Smart Home Devices
The global smart home market is experiencing significant growth. Reports indicate that the market value is projected to reach several billions of dollars in the coming years, driven by increasing consumer adoption and technological advancements. Factors like rising internet penetration, technological advancements in artificial intelligence, and expanding wireless connectivity networks contribute to the growth potential. The potential of this sector for innovation and development is substantial.
Comparison of Economic Impacts of Smart Homes in Different Regions
The economic impact of smart home adoption varies significantly across different regions. Developed countries, with higher internet penetration and technological infrastructure, are typically experiencing faster adoption rates. Emerging economies, while facing challenges in infrastructure and accessibility, also demonstrate a growing demand for smart home solutions, potentially stimulating local manufacturing and technological innovation. Differences in infrastructure, internet access, and economic development create variations in the speed and depth of smart home adoption.
Data on Market Value and Growth Potential
The global smart home market is experiencing steady growth. While precise figures vary depending on the reporting agency, estimates suggest an annual growth rate of approximately 15% in recent years. This projected growth rate signifies a dynamic and promising sector for investment and job creation. Multiple research reports from reputable market analysis firms provide detailed data and projections on the growth and market value of smart home technology.
Growth is driven by increasing demand and technological improvements.
Consumer Adoption and Market Trends
Consumer adoption of smart home technology is steadily increasing, driven by factors ranging from convenience and enhanced security to the allure of innovative features. This burgeoning market presents both significant opportunities and challenges for manufacturers and retailers. The journey toward widespread smart home integration is marked by both rapid progress and nuanced consumer behaviors.
Consumer Adoption Rates
Consumer adoption rates of smart home technology are demonstrably increasing, though at varying paces across different regions and demographics. Early adopters were often tech-savvy individuals, but now the market is broadening to include a more diverse range of consumers. Factors like affordability, ease of use, and the perceived value proposition significantly impact adoption rates.
Factors Influencing Consumer Decisions
Several key factors influence consumer decisions regarding smart home adoption. Ease of integration with existing systems, reliable performance, and a user-friendly interface are paramount considerations. Furthermore, compelling functionalities, such as energy efficiency and security enhancements, often drive consumer interest. The perceived value for money, alongside demonstrable benefits, is also a crucial element in the purchasing decision.
Market Trends and Predictions
Market trends suggest that the smart home market is expanding rapidly. Growing interest in voice-activated assistants, integration with other smart devices, and seamless home automation are expected to continue driving demand. Furthermore, increasing affordability of smart devices and improved interoperability are catalysts for broader adoption. The future holds potential for even more advanced functionalities and a greater focus on personalized experiences.
Successful Marketing Campaigns, Smart home technology trends
Numerous successful marketing campaigns have been instrumental in driving smart home adoption. Effective campaigns frequently highlight the practical benefits of smart home technology, showcasing how it enhances daily life, and demonstrating ease of use and integration. Targeting specific demographics with tailored messaging is critical for success. For instance, emphasizing energy savings to environmentally conscious consumers or highlighting security features for families has proven highly effective.
Market Share Data and Projections
| Smart Home Device Category | Current Market Share (estimated) | Projected Market Share (2025 estimate) |
|---|---|---|
| Smart Lighting | 25% | 35% |
| Smart Speakers | 18% | 25% |
| Smart Thermostats | 12% | 20% |
| Smart Security Systems | 10% | 15% |
The table above provides a snapshot of estimated current and projected market share for various smart home device categories. These figures are based on industry reports and analysis, and further refinement and adjustments will likely occur as the market continues to evolve.
Environmental Sustainability of Smart Homes
Smart home technology, while offering convenience and enhanced living, presents a dual nature regarding its environmental impact. Careful consideration of energy consumption and waste reduction is crucial for realizing the full potential of this technology in a sustainable future. The potential for significant environmental benefits exists alongside the need for responsible design and operation.Smart home systems, when implemented effectively, can significantly contribute to reducing the environmental footprint of homes.
Key to this positive impact is a proactive approach to energy management and waste minimization. A focus on energy efficiency is not just a trend, but a critical element in ensuring a sustainable future for smart home technology.
Environmental Impact of Smart Home Devices
Smart home devices, though often perceived as sophisticated, can have an environmental impact. Manufacturing processes and disposal of components contribute to waste generation. The energy consumption during operation, though often minimized by smart features, should be factored into the overall environmental assessment. Furthermore, the energy consumption for data transmission and processing by the connected devices, while potentially minimal, should not be overlooked.
Understanding the lifecycle assessment of these devices is critical to a comprehensive environmental evaluation.
Potential for Energy Efficiency in Smart Homes
Smart homes offer significant potential for promoting energy efficiency. Sophisticated systems can optimize energy use by dynamically adjusting lighting, heating, and cooling based on real-time occupancy and environmental conditions. This proactive approach to resource management can lead to considerable savings in energy consumption. Predictive maintenance of appliances can also minimize energy waste.
Smart home tech is evolving rapidly, pushing boundaries in convenience and efficiency. Considering how these advancements impact our living spaces, it’s crucial to consider home design ideas, like how to best integrate smart features into existing or new homes. Home design ideas are crucial for maximizing the benefits of smart technology, ensuring seamless functionality and a stylish aesthetic.
Ultimately, smart home technology is shaping the future of living spaces.
Smart Home Features Minimizing Environmental Impact
Numerous smart home features contribute to a smaller environmental footprint. Smart thermostats, for instance, automatically adjust temperature settings based on occupancy and weather patterns. Smart lighting systems can reduce energy use by automatically dimming or turning off lights when not needed. Smart appliances can optimize energy consumption during operation. Integration with renewable energy sources, like solar panels, further enhances the sustainable capabilities of smart homes.
Role of Smart Home Technology in Reducing Energy Consumption
Smart home technology plays a crucial role in reducing energy consumption. Automated systems can monitor and manage energy use in real-time, enabling users to identify and address energy-intensive activities. Remote control capabilities allow users to adjust settings and optimize energy consumption from anywhere. Smart home hubs can aggregate data from various devices, allowing users to gain insights into their energy usage patterns.
The data-driven approach to energy management facilitates informed decision-making, reducing overall consumption.
Smart Homes and Waste Management
Smart homes can contribute to waste management through several approaches. Smart appliances, like smart refrigerators, can alert users to food spoilage, reducing food waste. Smart bins can monitor fill levels and schedule waste collection, minimizing unnecessary trips and optimizing waste management processes. Integration with smart recycling systems can enhance waste sorting and disposal practices.
Design and Implementation Considerations
Smart home systems, while offering convenience and automation, demand careful planning and implementation to avoid pitfalls. A well-designed smart home integrates seamlessly with the homeowner’s lifestyle and existing infrastructure, maximizing functionality and minimizing potential issues. Effective implementation hinges on thorough design considerations, encompassing everything from initial planning to ongoing maintenance.
Different Smart Home Designs
Various smart home designs cater to different needs and budgets. A minimalist approach might focus on essential features like lighting and temperature control, while a comprehensive system could integrate appliances, security systems, and entertainment devices. Furthermore, custom designs can be tailored to specific requirements, such as accessibility features for individuals with disabilities or enhanced energy management solutions. Examples include a “smart kitchen” with integrated appliances and automated cooking routines, a “smart living room” incorporating advanced entertainment systems and automated lighting, or a “smart home office” featuring integrated communication and productivity tools.
Steps in Installing and Implementing a Smart Home System
A well-structured installation process ensures a smooth transition to a smart home environment. Initial steps typically involve assessing the existing infrastructure, identifying needs, and selecting appropriate smart devices. This is followed by device setup and configuration, integrating devices into a central control system, and testing the entire system. Finally, ongoing maintenance and troubleshooting are crucial for ensuring long-term system reliability.
Approaches to Smart Home System Design
Different approaches to smart home system design vary in complexity and control. A centralized approach employs a single hub or platform to manage all devices, simplifying control but potentially limiting scalability. A decentralized approach, on the other hand, allows for greater flexibility but requires more complex integration and management. A hybrid approach combines elements of both, offering a balance between centralized control and decentralized flexibility.
For instance, a home might use a central hub for lighting and security while employing individual controllers for appliances.
Importance of Planning and Design
Proper planning is essential for a successful smart home implementation. A well-defined plan minimizes installation errors and ensures the system aligns with the homeowner’s lifestyle and future needs. This includes considering factors like the home’s layout, existing electrical infrastructure, and the homeowner’s preferences. Careful planning reduces potential conflicts and ensures a harmonious integration of smart technology into the existing living space.
Security Considerations for Smart Home Systems
Security is paramount in any smart home system. Robust security measures are crucial to protect sensitive data and prevent unauthorized access. Implementing strong passwords, enabling multi-factor authentication, and regularly updating software are essential security precautions. Moreover, choosing reputable manufacturers and adhering to industry best practices in security design are also vital. Using encryption for data transmission, regularly reviewing access permissions, and incorporating intrusion detection systems can all contribute to enhanced security.
A robust security strategy will protect the home and its occupants from potential threats.
Final Summary
In conclusion, smart home technology trends are evolving at a rapid pace, impacting various aspects of our lives. From connectivity advancements to AI integration and security considerations, the future of smart homes promises exciting possibilities. However, responsible implementation and addressing potential challenges are essential for realizing the full potential of this transformative technology.
General Inquiries
What are the biggest security risks associated with smart home devices?
Security vulnerabilities can stem from weak passwords, outdated software, and insecure network configurations. Hackers can potentially gain access to control systems, potentially compromising privacy and even physical security.
How can I make my smart home more energy efficient?
Smart home systems can optimize energy usage by adjusting lighting, temperature, and appliance operation based on real-time conditions and user schedules. Integration with renewable energy sources further enhances energy efficiency.
What are the economic benefits of adopting smart home technology?
Smart homes can lead to reduced energy bills, increased home value, and potential job creation in the technology sector. They also offer opportunities for businesses and consumers to enhance efficiency and convenience.
How does AI personalize the smart home experience?
Machine learning algorithms analyze user behavior to tailor lighting, temperature, and other settings for optimal comfort and convenience. Voice assistants further enhance personalization through voice commands and learning user preferences.





